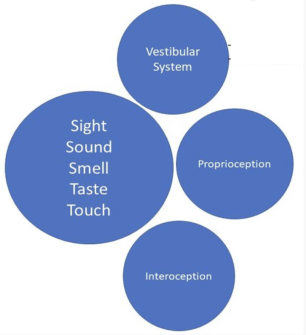
The 8 Senses and Interoception
The 8 SENSES include
- the 5 Senses we usually think about (seeing, hearing, smelling, tasting, and feeling)
- plus 3 equally important “body” senses:
• VESTIBULAR (information about motion and balance),
• PROPRIOCEPTION (information about position – from muscles and joints), and
• INTEROCEPTION (body-organ awareness).
INTEROCEPTION or organ awareness is the ability to sense the condition of one’s body – to feel whether we are hot or cold, hungry or full or thirsty.
INTEROCEPTION also includes the ability to feel pain and know where the pain is coming from.
Loss of INTEROCEPTION is a hallmark of TRAUMA and often related to Eating Disorders and Chronic Pain.
REBUILDING INTEROCEPTION
People can rebuild INTEROCEPTION through a
combination of BRAIN-BODY activities such as
- MINDFULNESS
- YOGA, and
- TRAUMA Processing therapy.
RESOURCES
D'Andrea (2022). To thine own self be true: interoceptive accuracy and interpersonal problems. Borderline Personal Disord Emot Dysregul. Interoceptive accuracy is the ability to correctly perceive body states, such as how quickly one's heart is beating, and has been associated with emotional experience and various crucial social capacities. Similarly, parasympathetic activity is related to social processing and inhibition of impulses. Lack of interoceptive accuracy and/or inability to flexibly self-regulate (awareness of one's emotions) may contribute to interpersonal problems.
Harricharan (2021) How Processing of Sensory Information From the Internal and External Worlds Shape the Perception and Engagement With the World in the Aftermath of Trauma: Implications for PTSD Front Neurosci. Neural alterations may underlie how sensations are experienced among traumatized individuals, including those from the outside world (e.g., touch, auditory, and visual sensations) and the internal world of the body (e.g., visceral sensations, physical sensations associated with feeling states). Alterations in the neural pathways important for the processing of sensations originating in the outer and inner worlds may have cascading effects on the performance of higher-order cognitive functions, including emotion regulation, social cognition, and goal-oriented action, thereby shaping the perception of and engagement with the world.
Rabellino (2020) Peripersonal Space and Bodily Self-Consciousness: Implications for Psychological Trauma-Related Disorders. Front Neurosci. Peripersonal space (PPS) is an essential component of bodily self-consciousness that allows us to perform actions in the world (e.g., grasping and manipulating objects) and protect our body while interacting with the surrounding environment. Multisensory processing plays a critical role. Review of (1) the behavioral and neurobiological literature surrounding trauma-related disorders and its relevance to PPS; and (2) outline future research directions aimed at examining altered states of bodily self-consciousness in trauma related-disorders.
test